Internship
An internship is a temporary work opportunity provided by organizations to students or professionals, allowing them to gain practical experience in a specific field or industry.
Internships have become a pivotal stepping stone in today's competitive job market, offering immense benefits for both employers and individuals looking to kickstart their professional journey. Whether you're a recruiter searching for top talent or a candidate seeking valuable career opportunities, this comprehensive blog has got you covered.
So, let's delve into the intricacies of internships, from providing valuable insights, expert tips, and actionable advice to unlocking the secrets to a successful internship experience!
What is an Internship?

An internship is a structured and supervised work experience designed to provide individuals, often students or recent graduates, with practical exposure to a particular industry, job role, or field of study. Allowing participants to gain hands-on experience, develop relevant skills, and explore potential career paths, the Internship acts as a bridge between academic learning and real-world application,
Internships can be offered by various organizations, including companies, non-profits, government agencies, and startups. They can vary in duration, ranging from a few weeks to several months, depending on the organization's requirements and the nature of the work involved.
During an internship, participants are typically assigned specific tasks and projects related to their area of study or interest. They work under the guidance of experienced professionals who act as mentors, providing valuable insights, feedback, and support throughout the internship period.
Why are Internships Important?
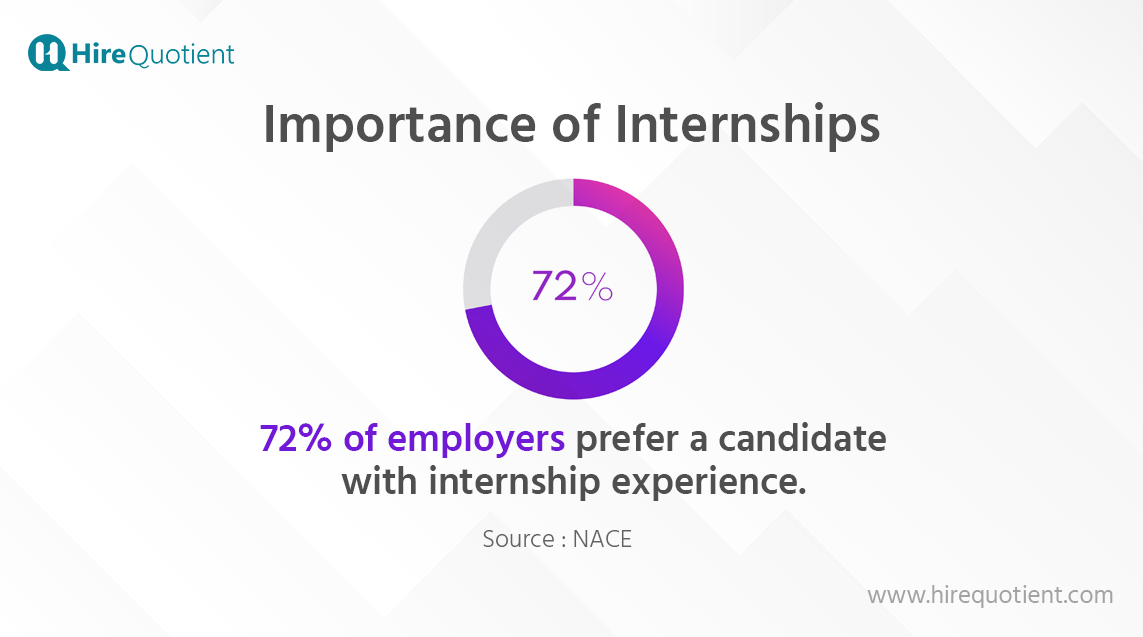
Internships play a crucial role in the professional development of individuals, serving as a bridge between academia and the corporate world. They offer valuable opportunities for students and recent graduates to enter the workforce. Moreover, those seeking to transition into a new career can leverage internships to kickstart their journey in a different field. The significance of internships becomes evident through the 2023 NACE Internship & Co-Op Report -
- Interns are more likely to be offered a full-time job after their internship than those who do not have internship experience.
- 60% of college graduates who had an internship before graduation were employed within six months of graduation.
- The average starting salary for college graduates with internship experience is $5,000 more than those without internship experience.
- Internships can help you develop your professional skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving.
- Internships can help you network with professionals in your field and build relationships that could lead to future job opportunities.
Benefits of Internship for the Employer
- Access to Fresh Perspectives and Ideas: Interns bring a fresh perspective to the organization, often coming with new ideas, innovative thinking, and the latest knowledge from their academic backgrounds.
- Talent Pipeline for Future Hiring Needs: Internship programs serve as a talent pipeline, allowing employers to identify and evaluate potential future employees. By offering internships, companies can assess skills, work ethic, and cultural fit candidates before committing to a full-time employment offer.
- Enhanced Employee Mentorship and Leadership Skills: Having interns in the workplace provides an opportunity for employees to take on mentorship roles, which can lead to the development of their leadership skills. When employees mentor interns, they gain experience in guiding others, fostering teamwork, and providing constructive feedback. This contributes to a more cohesive and skilled workforce.
- Increased Productivity and Cost-Effectiveness: Interns can assist with various tasks and projects, allowing regular employees to focus on more strategic or specialized responsibilities. This increased productivity can lead to improved overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness for the organization.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: Hiring interns can be a cost-effective approach for completing short-term projects and tasks. Compared to hiring full-time employees, internships can provide significant cost savings on salaries, benefits, and other employment-related expenses.
Benefits of Internship for the Professional/Candidate
- Hands-On Experience and Skill Development: Internships provide candidates with practical, hands-on experience in their chosen field, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations.
- Exploring Career Paths and Industry Insights: Internships offer candidates the opportunity to explore different career paths and industries. They can gain valuable insights into the day-to-day operations, company culture, and specific roles, helping them make informed career decisions.
- Networking and Professional Connections: During internships, candidates can build professional networks by interacting with colleagues, mentors, and industry professionals. These connections can lead to future job opportunities and career growth. In a survey conducted by LinkedIn, 70% of people were hired at a company where they had a connection.
- Enhanced Soft Skills: Internships not only focus on technical skills but also help candidates develop essential soft skills such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and time management.
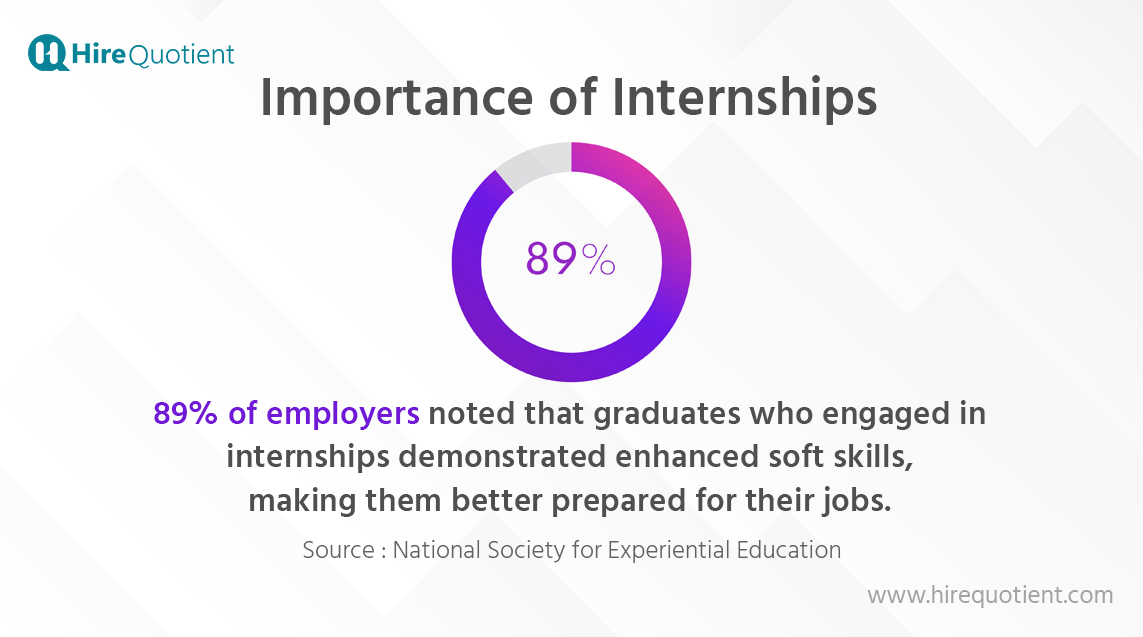
- Confidence Building: By successfully completing tasks and projects during internships, candidates gain confidence in their abilities and potential to excel in their chosen field. This increased self-assurance can positively impact their performance in future job roles.
- Resume Enhancement: Having relevant internship experience on a resume can significantly improve a candidate's chances of being considered for job opportunities.
- Personal Growth and Professional Development: Internships provide opportunities for candidates to set goals, receive feedback, and identify areas for improvement. This reflective process contributes to their personal growth and continuous professional development.
Internships vs. Other Opportunities
When considering career development and gaining practical experience, individuals often have several options to choose from. Let's compare internships with other opportunities to understand their respective advantages and limitations:
- Part-Time Jobs: Part-time jobs are employment opportunities that require fewer working hours than full-time positions. They can be within the same field of interest or unrelated to the candidate's career goals.
- Volunteering: Volunteering involves contributing time and skills to a charitable or non-profit organization without financial compensation.
- Apprenticeships: Apprenticeships are formal training programs that combine on-the-job learning with classroom instruction. They are often used in skilled trades and technical fields.
- Co-ops: Co-op programs, short for cooperative education programs, are long-term work experiences integrated into an academic curriculum. Students alternate periods of full-time work at a company or organization with periods of study at their educational institution.
Comparing Internships, Part-Time Jobs, Volunteering, Apprenticeships, and Co-op Programs:
Duration:
- Internships: Typically short-term, ranging from a few weeks to a few months.
- Part-Time Jobs: Ongoing or fixed-term, with flexible working hours.
- Volunteering: Varies from short-term projects to long-term commitments.
- Apprenticeships: These can last for several months to several years, depending on the trade or profession.
- Co-op Programs: Longer-term, often lasting for several semesters or academic terms.
Academic Integration:
- Internships: Not always integrated into an academic program, although some universities may offer academic credits for internships.
- Part-Time Jobs: No direct academic integration.
- Volunteering: Typically not integrated into academic programs, although some educational institutions may recognize community service for credit.
- Apprenticeships: More commonly associated with vocational or technical training, directly linked to academic and certification requirements.
- Co-op Programs: Integrated into the academic curriculum, with structured periods of work and study.
Skill Development:
- Internships: Emphasize skill development and hands-on learning related to the candidate's career interests.
- Part-Time Jobs: These may provide general workplace skills, but not always directly related to the candidate's desired career path.
- Volunteering: Focus on developing interpersonal skills and a sense of social responsibility, with the potential to acquire transferable skills.
- Apprenticeships: Target specific vocational skills and technical competencies in a particular trade or industry.
- Co-op Programs: Offer a well-rounded blend of academic knowledge and practical skills development.
Compensation:
- Internships: These can be paid or unpaid, depending on the organization and local labor laws.
- Part-Time Jobs: Offer financial compensation for the hours worked.
- Volunteering: Typically unpaid, but may provide non-monetary rewards such as personal fulfillment and community impact.
- Apprenticeships: Often paid positions, as apprentices are considered employees while receiving training.
- Co-op Programs: Co-op students may receive wages or stipends during their work terms.
Career Focus:
- Internships: Primarily aimed at providing career-related experience and networking opportunities.
- Part-Time Jobs: May or may not align with the candidate's career interests.
- Volunteering: Focused on community service and making a positive impact, but may not directly relate to a specific career path.
- Apprenticeships: Centered on vocational training and preparing candidates for skilled trade professions.
- Co-op Programs: Integrate academic learning with real-world work experience to support career readiness.
How to Hire Interns? Tips and Tricks
Hiring interns for startups, especially for marketing and sales roles, can be a great way to bring fresh talent and energy to your business. Here are some tips and tricks to help you successfully hire interns for these specific roles:
- Craft Clear Job Descriptions: Write detailed job descriptions for both marketing and sales intern positions. Clearly outline the responsibilities, required skills, and any specific qualifications. Highlight the learning opportunities and growth potential they will gain from the internship.
- Utilize University Career Centers: Reach out to local universities and colleges with strong marketing and business programs. Career centers often have internship posting services and can help you connect with potential candidates.
- Online Job Boards and Internship Websites: Post your internship opportunities on popular job boards and websites dedicated to internships. Examples include LinkedIn, Indeed, Glassdoor, and Internships.com.
- Networking and Referrals: Leverage your professional network and ask for referrals from employees, business partners, or friends. Referrals can often lead to finding candidates who are already familiar with your company's values and goals.
- Internship Fairs and Events: Participate in internship fairs and industry-related events. This gives you the chance to interact with potential candidates face-to-face and promote your startup and its internship opportunities.
- Use Social Media: Leverage your company's social media platforms to announce internship openings. Engage with potential candidates who show interest and answer their questions promptly.
- Utilize Sourcing Tools: Automated talent sourcing tools powered by Generative AI and Chat-GPT are trending recruitment tools that can come in handy when looking for interns.
Paid Internship Guidelines For Employers
Paid internships offer numerous benefits to both employers and interns. When setting up a paid internship program, it's important for employers to follow certain guidelines to ensure compliance with labor laws and create a positive experience for the interns. Here are some guidelines for employers considering paid internships:
- Define the Internship Program: Clearly outline the objectives and scope of the internship program. Identify the specific projects or tasks the interns will be working on and the skills they are expected to develop during their internship.
- Internship Duration and Hours: Determine the length of the internship and the number of working hours per week. Ensure that the schedule aligns with any applicable labor laws or regulations.
- Fair Wage: Offer a competitive wage or stipend that is in line with industry standards and local regulations. The wage should be commensurate with the work and responsibilities assigned to the interns.
- Educational Value: Emphasize the educational aspect of the internship. The primary focus of the internship should be on learning and gaining valuable experience, rather than just providing cheap labor.
- Internship Agreement: Draft a written internship agreement that outlines the terms and conditions of the internship, including compensation, working hours, and any company policies the interns must adhere to.
- Compliance with Labor Laws: Familiarize yourself with the labor laws and regulations governing internships in your region. Ensure that the internship program adheres to minimum wage laws, overtime regulations, and other applicable labor standards.
- Avoid Misclassification: Ensure that the interns are properly classified as interns and not as regular employees. Interns should not be performing duties that would typically be done by paid staff members.
- Supervision and Mentorship: Assign a supervisor or mentor to each intern who can provide guidance, feedback, and support throughout the internship. Regular check-ins can help interns stay on track and meet their learning goals.
- Equal Opportunity and Inclusivity: Promote diversity and inclusion in your internship program. Avoid any form of discrimination in the hiring process or during the internship.
- Real Projects and Responsibilities: Offer interns meaningful tasks and projects that align with their interests and career goals. Provide opportunities for them to contribute to the company's success and growth.
- Feedback and Evaluation: Provide regular feedback to interns on their performance and progress. Conduct a formal evaluation at the end of the internship to help interns understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Maintain a Safe Working Environment: Ensure that the workplace is safe and conducive to learning. Comply with health and safety regulations to protect the well-being of interns and all employees.
- Confidentiality and Intellectual Property: Discuss and clarify any confidentiality or intellectual property agreements that interns need to adhere to during their internship.
- Exit Strategy: Outline the end of the internship program, including a clear conclusion or potential next steps for the interns after completing their internship.
Read: Recruitment Guidelines
HR Policies For Internship
HR policies for internships are crucial to ensure a positive and productive experience for both the interns and the organization. Here are some essential HR policies to consider when implementing an internship program:
- Equal Opportunity Policy: Emphasize that the organization provides equal opportunities to all candidates, regardless of their race, gender, ethnicity, religion, disability, or any other protected characteristic. Ensure that the selection process is fair and unbiased.
- Code of Conduct: Establish a clear code of conduct that outlines expected behavior from interns, including professionalism, respect for others, confidentiality, and adherence to company policies.
- Work Hours and Attendance: Define working hours and attendance expectations for interns. Clarify any rules regarding punctuality, breaks, and time off.
- Confidentiality and Data Protection: Communicate the importance of maintaining confidentiality for all company information and data. Ensure interns understand their responsibilities regarding data protection and handling sensitive information.
- Safety and Health Policies: Educate interns about workplace safety and health guidelines. Provide information on emergency procedures and how to report any accidents or incidents.
- Anti-Harassment Policy: Make it clear that harassment of any kind, including sexual harassment, is strictly prohibited. Provide a mechanism for reporting harassment complaints confidentially.
- Internship Duration and Objectives: Define the length of the internship and the specific objectives and learning outcomes the interns are expected to achieve during their tenure.
- Supervision and Feedback: Outline the structure for supervision and feedback. Assign a supervisor or mentor to each intern who can provide regular feedback, guidance, and support.
- Compensation and Benefits: Specify the compensation or stipend offered to interns, along with any benefits they may be entitled to during their internship period.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Clearly communicate the organization's policies regarding intellectual property rights, ensuring that any work created by interns during the internship belongs to the company.
- Social Media and Public Communication: Educate interns on the company's policies regarding social media usage and public communication. Emphasize the importance of representing the company in a positive light.
- Internship Termination Policy: Establish a policy for the termination of internships, outlining the circumstances under which an internship may be terminated and the notice required.
- Performance Evaluation: Explain the process of performance evaluation, including the criteria used to assess interns' progress and any opportunities for extension or future employment.
- Compliance with Labor Laws: Ensure that all HR policies are in compliance with relevant labor laws, including minimum wage requirements, working hours restrictions, and other employment regulations.
- Exit Process: Provide a clear exit process for interns, including exit interviews to gather feedback and discuss their overall experience.
- Training and Development Opportunities: Communicate any training and development opportunities available to interns during their internship to enhance their skills and knowledge.
Read: Company Policies
Internship Certificate Format
Internship Certificate
This is to certify that [Intern's Full Name] has successfully completed the [Internship Program Name] at [Company Name]. The internship was undertaken from [Start Date] to [End Date].
Internship Details:
- Intern's Full Name: [Intern's Full Name]
- Internship Program Name: [Internship Program Name]
- Internship Start Date: [Start Date]
- Internship End Date: [End Date]
- Department/Division: [Department/Division Name]
- Supervisor/Mentor: [Supervisor/Mentor's Full Name]
- Internship Location: [City, State]
Internship Objectives:
During the internship, [Intern's Full Name] demonstrated a keen interest in [briefly describe the main objectives and focus of the internship]. The intern actively participated in [mention tasks, projects, or responsibilities undertaken by the intern].
Key Accomplishments:
- [List some of the significant achievements or contributions made by the intern during the internship].
Skills Developed:
Throughout the internship, [Intern's Full Name] exhibited a strong commitment to learning and showed remarkable improvement in the following areas:
- [List the key skills developed by the intern during the internship, such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, etc.].
Overall Performance:
The intern's performance during the internship period was [mention outstanding/excellent/commendable/very good/good]. [He/She] consistently demonstrated dedication, enthusiasm, and a willingness to take on new challenges.
Conclusion:
We express our sincere appreciation to [Intern's Full Name] for [his/her] valuable contributions to [Company Name]. [He/She] has been an asset to our team, and [his/her] efforts have positively impacted our projects and goals.
Acknowledgment:
We acknowledge the successful completion of the internship by awarding this certificate as a token of recognition for [Intern's Full Name]'s commitment and dedication.
_____________________________
[Supervisor/Mentor's Full Name]
[Designation]
[Company Name]
_____________________________
[Your Name]
[Designation]
[Company Name]
Date: [Date of Certificate Issuance]
Note: This internship certificate is issued in compliance with the policies and guidelines of [Company Name].
Ways To Find an Internship
Finding an internship can be a rewarding experience that kick-starts your career and provides valuable hands-on learning. Here are some effective ways to find an internship:
- Online Job Boards: Check out popular online job boards such as LinkedIn, Indeed, Glassdoor, and Internships.com. Use relevant keywords and filters to narrow down your search.
- Company Websites: Many companies post their internship openings directly on their websites. Visit the career or job opportunities section of companies you are interested in.
- University Career Centers: Utilize your university's career center resources. They often have dedicated internship listings and can connect you with employers seeking interns.
- Networking: Leverage your personal and professional network. Inform friends, family, professors, and acquaintances that you are looking for an internship. Networking events and industry meetups are also excellent opportunities to make connections.
- Internship Fairs: Attend internship fairs and career events hosted by universities, companies, or organizations. These events bring employers and potential interns together.
- Internship Programs: Look for internship programs run by governmental organizations, non-profits, and private companies. These programs often provide structured and meaningful learning experiences.
- Cold Applications: If there's a specific company you'd like to intern with, consider sending a targeted cold application. Tailor your resume and cover letter to showcase your skills and passion for their industry.
- Faculty Recommendations: Speak with your professors or academic advisors about potential internship opportunities. They might have contacts in the industry or know about internships available through their professional networks.
Tips For Getting an Internship
Getting an internship can be competitive, but with the right approach, you can increase your chances of landing one. Here are some valuable tips to help you secure an internship:
- Start Early: Begin your internship search well in advance, as many companies start recruiting interns months before the internship start date.
- Identify Your Interests: Determine the industries, roles, and skills you want to explore during your internship. Having a clear focus will help you target relevant opportunities.
- Update Your Resume and LinkedIn Profile: Tailor your resume to highlight relevant coursework, skills, extracurricular activities, and any previous work experience. Optimize your LinkedIn profile to showcase your achievements and interests.
- Network: Leverage your personal and professional network to discover potential internship opportunities. Attend career fairs, and networking events, and join relevant online communities.
- Utilize University Resources: Take advantage of your university's career center, internship programs, and workshops. They can provide valuable guidance and connections.
- Research Companies: Identify companies that align with your career goals and values. Research their internship programs, culture, and recent projects to demonstrate genuine interest during interviews.
- Customize Applications: Tailor your application for each internship you apply to. Highlight specific skills and experiences that match the requirements of the role.
- Write a Strong Cover Letter: Craft a compelling cover letter that showcases your passion for the industry, explains why you're interested in the company, and demonstrates how your skills align with the internship.
- Prepare for Interviews: Practice common interview questions and be ready to discuss your experiences, skills, and career goals. Research the company and be prepared to ask thoughtful questions.
In a Nutshell,
For candidates and professionals, internships provide invaluable hands-on experience, skill development, and exposure to real-world challenges. They serve as stepping stones towards fulfilling career paths, offering opportunities to network with industry experts and secure future employment prospects.
Remember, securing an internship is not merely about chance; it requires dedication, perseverance, and a strategic approach. By honing your resume, crafting compelling cover letters, and actively seeking opportunities through various channels, you can increase your chances of landing the ideal internship that aligns with your goals.