Employee
A person under a contract to provide work to a business in return for wages or salary.
"Always treat your employees exactly as you want them to treat your best customers." - Stephen R. Covey
In the ever-evolving and dynamic world of work, the term "employee" holds a central position, defining the backbone of modern organizations. It represents individuals whose dedication, skills, and commitment breathe life into the corporate machinery, propelling businesses forward. From bustling office spaces to remote corners of the digital realm, employees play an irreplaceable role in shaping the success and growth of any organization.
So let us delve into understanding the definition and and meaning of an employee along with their benefits and rights at workplace.
What is an Employee?

Employees are the lifeblood of any organization, bringing their skills, expertise, and dedication to fulfill specific roles within the company. They share several core characteristics that distinguish them from other working arrangements. Let's delve into these defining traits:
- Employment Relationship: One fundamental characteristic of an employee is their formal relationship with the employer, governed by an employment contract. This contract outlines their rights, responsibilities, and the terms and conditions of their engagement with the company.
- Supervision and Control: Employees work under the direct supervision and control of the employer. They are guided by the company's policies, procedures, and management, which help maintain a structured work environment.
- Regular Wages or Salary: Employees receive regular wages or salaries for their work, either on an hourly, weekly, or monthly basis. This predictable income fosters financial stability and incentivizes productivity.
- Tax Withholding: Employers withhold taxes from employees' wages, making them eligible for various tax benefits and social security contributions.
- Benefits and Perks: Employees often receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other perks as part of their compensation package.
The Employee-Employer Relationship
The dynamic between employees and employers plays a vital role in shaping workplace culture and productivity. Let's explore some trends related to the employee-employer relationship:
- Employee Engagement: Employee engagement is a crucial aspect of a productive workforce. According to Gallup's State of the Global Workplace report, only 15% of employees worldwide are engaged in their jobs, indicating a significant room for improvement in fostering commitment and enthusiasm among employees.
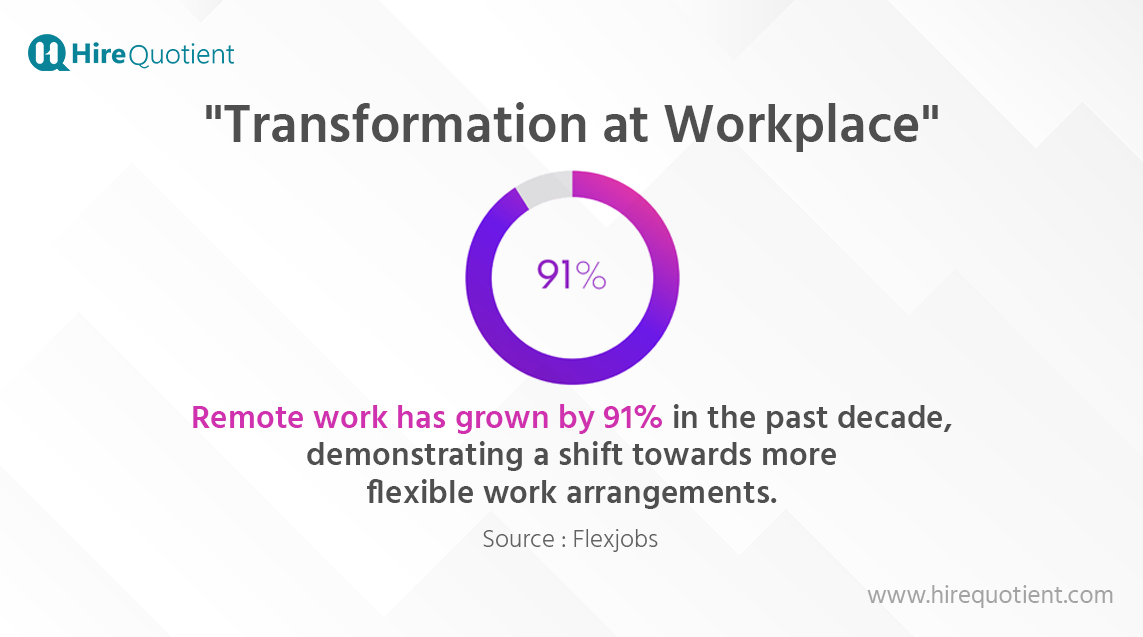
- Remote Work Trends: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work. According to a survey by FlexJobs, remote work has grown by 91% in the past decade, demonstrating a shift towards more flexible work arrangements.
- Employee Turnover: High employee turnover can be detrimental to an organization's stability and growth. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the average turnover rate in the United States across all industries was 57.7% in 2020, emphasizing the importance of employee retention strategies.
Types of Employees
Full-Time Employees
Definition: Full-time employees are individuals who work a standard number of hours per week, typically around 35 to 40 hours. They are considered permanent staff and enjoy the stability and security of long-term employment.
Roles and Benefits:
- Full-time employees often hold crucial roles within the organization, contributing to its day-to-day operations and long-term objectives.
- They may receive comprehensive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other incentives.
- Employers value their dedication and commitment, making full-time employees essential for building a strong company culture.
Part-Time Employees
Definition: Part-time employees work fewer hours than full-time employees, usually less than 35 hours per week. They offer flexibility to both the employee and employer.
Roles and Benefits:
- Part-time employees are valuable for businesses with fluctuating workloads or seasonal demands, as they can fill in gaps without requiring full-time commitments.
- They may still be eligible for certain benefits, although they might be prorated based on their hours worked.
- Part-time arrangements allow employees to pursue other interests or responsibilities outside of work, contributing to better work-life balance.
Gig-Workers
Definition: Gig workers, also known as temporary employees, are hired for a specific duration or project. These employees are hired to meet short-term demands during peak periods.
Roles and Benefits:
- Gig workers offer flexibility in managing variable workloads without the commitment of permanent positions.
- They bring specialized skills and expertise for particular projects or busy seasons, contributing to improved productivity.
- While they may not receive the same benefits as permanent employees, they gain valuable work experience and networking opportunities.
Contract Employees
Definition: Contract employees are hired on a contract basis to provide specialized services, often in fields such as IT, consulting, or creative industries.
Roles and Benefits:
- Contract employees offer unique expertise and skills, filling gaps in the organization's capabilities for specific projects or initiatives.
- They enjoy a higher level of independence in their work, often setting their own schedules and methods of operation.
- Contract arrangements allow organizations to access top talent without the long-term commitment of hiring full-time employees.
What are Employee Benefits?
Employee benefits are non-wage compensations provided by employers to their employees, in addition to their regular salary or wages. These benefits are offered as part of the overall compensation package to attract, retain, and motivate employees. Employee benefits go beyond monetary compensation and are designed to enhance the well-being, job satisfaction, and overall quality of life for the workforce. The specific benefits offered may vary depending on the company's size, industry, and regional regulations, but they typically encompass a wide range of offerings.
Types of Employees Benefits
Health and Wellness Benefits
- Health Insurance: One of the most crucial benefits, health insurance covers medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospitalization, prescription medications, and preventive care. Providing comprehensive health coverage promotes a healthy workforce and helps alleviate financial burdens during medical emergencies.
- Dental and Vision Insurance: Dental and vision benefits offer coverage for routine check-ups, corrective procedures, and vision aids like glasses or contact lenses. These benefits contribute to employees' overall health and help address vision-related issues.
- Mental Health Support: An increasing number of employers recognize the importance of mental health support. Offering employee assistance programs (EAPs), counseling services, or access to mental health resources helps employees cope with stress, anxiety, and other emotional challenges.
Read: What is Defined Benefit Plan?
Retirement and Pension Plans
- 401(k) Plans: 401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement savings accounts that enable employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income, often with employer matching contributions. These plans empower employees to save for their retirement, promoting financial security in the long run.
- Pension Plans: While less common in the private sector today, pension plans provide employees with a fixed monthly income during retirement, based on their years of service and salary history. Some public and government organizations still offer traditional pension plans to their employees.
- Employee Stock Options: Employee stock options provide an opportunity for employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price. This benefit aligns employees' interests with the company's success, fostering a sense of ownership and loyalty.
Read: What is Golden Handcuffs?
Professional Development Opportunities
- Training and Development Programs: Investing in training and development programs enhances employees' skills and knowledge, making them more valuable assets to the organization. These initiatives contribute to employee growth and job satisfaction.
- Educational Assistance: Educational assistance programs, such as tuition reimbursement or scholarships, support employees pursuing higher education or job-related certifications. This benefit fosters continuous learning and professional development.
- Career Advancement Opportunities: Providing internal career advancement opportunities allows employees to progress within the organization, promoting employee retention and loyalty.
Work-Life Balance Benefits
- Paid Time Off (PTO): Paid time off includes vacation days, sick leave, and personal days, allowing employees to take time away from work to rest, rejuvenate, or address personal needs.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work or flexible hours, enable employees to achieve a better work-life balance, contributing to improved job satisfaction and reduced stress.
- Parental Leave: Parental leave benefits support new parents by providing time off to bond with their newborns or adopted children. Offering parental leave demonstrates a commitment to supporting employees during significant life events.
What are Employee Policies?
Employee policies are a set of rules, guidelines, and procedures established by an organization to govern the conduct and behavior of its employees. These policies serve as a framework for defining acceptable and unacceptable behaviors in the workplace and outline the expectations and responsibilities of both the employees and the employer. Employee policies are typically documented in an employee handbook or policy manual, which is provided to employees upon joining the organization.
The main purposes of employee policies are:
- Clarifying Expectations: Policies provide clear guidelines on what is expected of employees in terms of behavior, performance, and adherence to company values and standards.
- Promoting Consistency: Policies ensure consistent treatment of employees across the organization, preventing favoritism or unfair practices.
- Mitigating Risks: Policies address legal and compliance issues, helping the organization comply with labor laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Protecting Rights: Employee policies outline the rights and responsibilities of both employees and the employer, ensuring fair treatment and protection for all parties involved.
Common types of employee policies include:
- Code of Conduct: The code of conduct sets out the ethical and behavioral standards expected from employees, promoting integrity and professionalism.
- Anti-Discrimination and Harassment Policy: This policy prohibits any form of discrimination or harassment based on factors such as race, gender, religion, or age, fostering a respectful and inclusive workplace.
- Attendance and Punctuality: This policy defines expectations regarding attendance, punctuality, and procedures for requesting time off or reporting absences.
- Dress Code: The dress code policy outlines appropriate attire for the workplace, ensuring a professional and consistent appearance.
- Internet and Social Media Use: This policy governs the appropriate use of company-owned technology and the responsible use of social media while representing the organization.
- Performance Management: The performance management policy outlines the process for evaluating and managing employee performance, including performance reviews and feedback mechanisms.
- Grievance and Complaints: This policy provides employees with a procedure for voicing grievances or complaints about work-related issues.
- Data Privacy and Security: This policy ensures the protection of sensitive information and data belonging to the organization, clients, or employees.
- Health and Safety: The health and safety policy outlines measures to maintain a safe and healthy work environment for all employees.
- Remote Work Policy: This policy provides guidelines and expectations for employees working remotely, addressing communication, productivity, and data security.
Employees' Rights and Protections
In any workplace, ensuring the well-being and fair treatment of employees is of paramount importance. Employees' rights and protections are established through labor laws, regulations, and employment policies to safeguard workers from unfair practices, discrimination, and exploitation in the workplace. These rights are designed to promote a balanced employer-employee relationship and create a conducive work environment. Let's delve deeper into some essential employees' rights and the protections in place to uphold them:
- Right to Non-Discrimination: Employees have the right to be treated fairly and equally, free from discrimination based on their race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or other protected characteristics. Anti-discrimination laws, such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in the United States, prohibit employers from making employment decisions based on these factors.
- Right to a Safe and Healthy Work Environment: Employees have the right to work in an environment that is free from hazards and dangers that could cause harm or injury. Employers are obligated to comply with health and safety regulations, implement safety measures, and provide proper training to protect employees' well-being.
- Right to Fair Compensation: Employees have the right to receive fair compensation for their work. This includes compliance with minimum wage laws and payment for overtime hours, as well as adhering to wage and hour laws that govern issues like payment frequency and withholding rules.
Read: What is mean wage?
- Right to Family and Medical Leave: Eligible employees have the right to take unpaid leave for qualifying family and medical reasons under the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) in the United States. Similar protections may exist in other countries to allow employees to attend to personal and family needs without fear of losing their jobs.
- Right to Freedom from Harassment: Employees have the right to work in an environment free from harassment, including sexual harassment, bullying, or any form of conduct that creates a hostile work environment. Employers are required to address and prevent such behavior and provide avenues for employees to report incidents.
- Right to Organize and Join Unions: Employees have the right to engage in collective bargaining, form or join labor unions, and participate in union activities. Labor laws protect employees' right to unionize and negotiate with their employers on workplace conditions, benefits, and other matters.
- Right to Privacy: Employees have a reasonable expectation of privacy concerning personal belongings, communications, and private information while at work. Employers should respect employees' privacy rights and ensure that any monitoring or surveillance activities are conducted legally and ethically
- Right to Whistleblower Protection: Employees who report illegal or unethical practices within their organization have the right to protection from retaliation. Whistleblower laws shield employees from adverse actions for disclosing information about wrongdoing or violations of the law.
- Right to Reasonable Accommodation: Employees with disabilities have the right to reasonable accommodation to perform their job duties. Employers must make appropriate adjustments to the workplace or job responsibilities to accommodate employees' disabilities, as long as it does not cause undue hardship for the employer.
- Right to Review Employment Records: Employees generally have the right to access their employment records, including performance evaluations, payroll records, and other relevant documents. This right allows employees to review and verify the accuracy of their employment records.
The Evolving Role & Responsibilities of Employees in Modern Organizations
Traditional hierarchical structures have given way to flatter, more agile setups, while technological advancements and shifting societal expectations have reshaped the expectations from employees. Embracing these changes, employees find themselves taking on new roles and responsibilities that contribute to the success and adaptability of their organizations. Let's explore the key aspects of the evolving role and responsibilities of employees in modern workplaces:
- Embracing Technology and Digital Transformation: Modern organizations are increasingly reliant on technology to drive efficiency, innovation, and productivity. Employees are expected to embrace new digital tools and platforms, adapt to remote work setups, and acquire digital literacy skills to navigate the digital landscape effectively.
- Empowering and Driving Innovation: Employees are no longer just passive participants in the workplace; they are encouraged to be active contributors to innovation and problem-solving. Organizations seek employees who are creative, open to experimentation, and willing to challenge the status quo.
- Nurturing a Culture of Collaboration: Collaboration has become a cornerstone of modern organizations. Employees are expected to work collaboratively across teams, departments, and even geographical boundaries. They must be effective communicators, active listeners, and willing to share knowledge and expertise for the greater good of the organization.
- Adapting to Remote Work and Virtual Collaboration: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work and virtual collaboration. Employees now need to be proficient in virtual communication, remote project management, and self-discipline to maintain productivity and cohesion within remote teams.
- Emphasizing Continuous Learning: In the face of rapidly evolving industries and technological advancements, employees are expected to embrace a culture of continuous learning. Taking charge of their professional development, employees pursue upskilling and reskilling opportunities to remain relevant and competitive in the job market.
- Balancing Work and Mental Health: Organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of employee well-being, including mental health. The evolving role of employees includes understanding the importance of work-life balance, managing stress, and seeking support when needed to maintain overall well-being.
- Fostering Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion: Employees are called upon to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion within the workplace. They play a vital role in fostering a culture that respects and values individual differences, creating an environment where all employees feel welcome and included.
The Future of Work and the Employee's Role
The future of work is rapidly evolving, shaped by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and changing global dynamics. As organizations adapt to this new landscape, the role of employees undergoes significant transformation. The employee of the future must possess a diverse set of skills and embrace a forward-thinking mindset to thrive in this dynamic environment. Let's delve into the key trends and the evolving role of employees in shaping the future of work:
Embracing Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The integration of automation and AI technologies in the workplace is reshaping job roles and tasks.
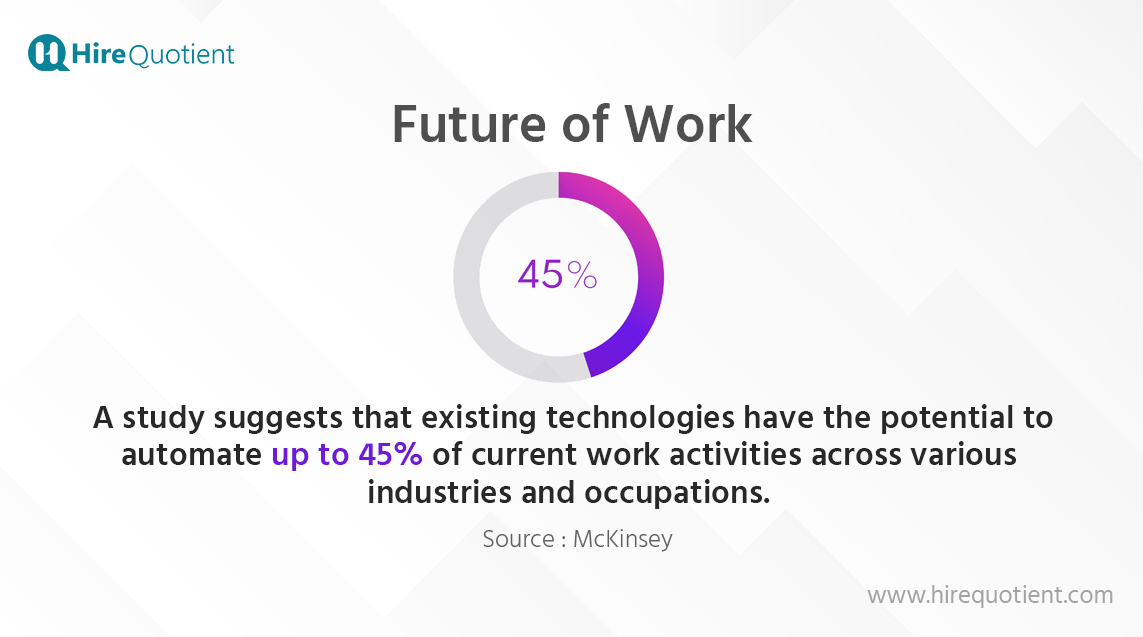
Employees must adapt by developing skills that complement automation, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and emotional intelligence. Rather than fearing automation, employees can focus on leveraging technology to augment their productivity and decision-making capabilities.
Navigating the Gig Economy and Remote Work
The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelancing, continues to expand. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, by 2025, the number of gig workers will exceed traditional employees in the U.S.
Employees in the future may increasingly choose freelance or project-based work arrangements for greater flexibility and autonomy. Remote work is also becoming more prevalent, offering employees the opportunity to work from anywhere. As a result, employees must develop strong time management, self-discipline, and virtual collaboration skills to excel in these non-traditional work arrangements.
Lifelong Learning and Upskilling:
The pace of technological advancement necessitates a commitment to lifelong learning and continuous upskilling. According to the World Economic Forum, 94% of business leaders expect employees to pick up new skills on the job.
Employers and employees alike must invest in training and development to stay relevant and adaptable to emerging technologies and market demands. The employee of the future embraces learning as a continuous journey, seeking opportunities to upskill and reskill throughout their career.
Embracing Inclusive Leadership
Diverse and inclusive workplaces drive innovation, employee satisfaction, and business performance. Employees are expected to embrace inclusive leadership, promoting diversity, and fostering a sense of belonging within their teams.
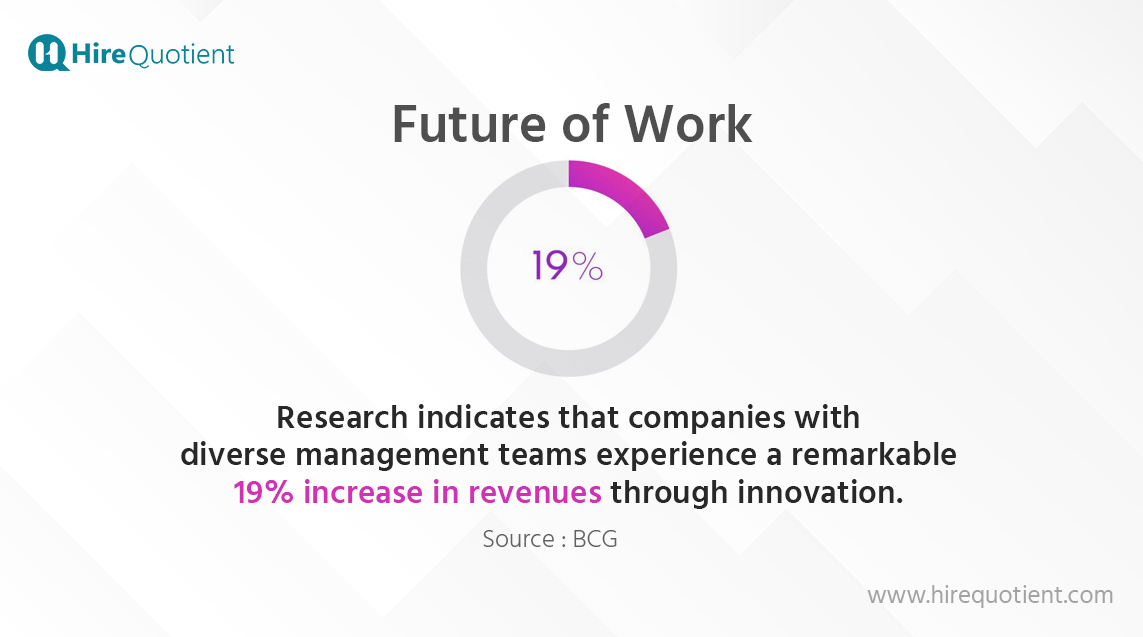
The employee of the future recognizes the importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion, fostering an environment that values different perspectives and experiences.
The Bottom Line
In exploring the multifaceted meaning and definition of 'employee,' we have come to appreciate the diverse roles and contributions individuals make within the vast spectrum of work settings. The concept of an employee extends far beyond the traditional nine-to-five job and permanent contracts. It encompasses a broad array of employment arrangements, each with its unique characteristics, rights, and responsibilities. You can learn more about enhancing the work-life of employees by reading up about employee engagement.
As we look towards the future, the evolving role of employees promises to be dynamic and transformative. Embracing automation, gig work, and remote arrangements, employees must adapt, upskill, and foster a culture of innovation to thrive in this ever-changing landscape.