Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to the ethical and voluntary initiatives taken by businesses and organizations to address their impact on society and the environment.
Remember the Global Skills Initiative by Microsoft?
The program aimed at helping people acquire digital skills and access in-demand jobs in the digital economy. The initiative was launched in June 2020, in response to the economic challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated the need for digital transformation and remote work.
We all know that companies are out there to make profits and flourish, but it's heartwarming to see how some of them genuinely care about the people and the planet. This was one such initiative by Microsoft. Similarly, there are hundreds of other initiatives that big brands take to cover that extra mile and do something wonderful for the planet.
These initiatives have an umbrella term called, Corporate Social Responsibility(CSR). Let us explore together the transformative potential of CSR and how it continues to redefine the role of companies in building a brighter, more sustainable, and inclusive future for all.
How to define Corporate Social Responsibility?

Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a concept that reflects a company's commitment to going beyond its primary objective of making profits. It entails a voluntary initiative where businesses take responsibility for their impact on society, the environment, and the well-being of the communities they operate in.
CSR involves a company considering and addressing its ethical, social, and environmental responsibilities in its day-to-day operations, decision-making processes, and overall business strategy. This can encompass various initiatives, such as supporting charitable causes, promoting sustainable practices, empowering marginalized communities, and contributing to the overall welfare of society.
The core essence of CSR lies in a company's genuine concern for the greater good, making efforts to create a positive impact on people's lives, fostering environmental sustainability, and actively engaging in philanthropic endeavors. By adopting CSR practices, companies can not only build trust with their customers and stakeholders but also play a vital role in fostering sustainable development and improving the world we live in.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility and Why is it Important?
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is essential for several compelling reasons. Embracing CSR practices can bring numerous benefits not only to the communities and the environment but also to the companies themselves. Here are some key reasons why CSR is important:
- Positive Impact on Society: CSR initiatives contribute to the well-being of society by addressing pressing social issues, supporting education, healthcare, poverty alleviation, and empowering marginalized communities. According to a survey conducted by Cone Communications, 89% of consumers are likely to switch brands to one associated with a good cause, indicating that companies that engage in CSR can build a positive reputation and attract more customers.
- Attracting Investment: Investors are increasingly considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors when making investment decisions. A study by MSCI found that companies with strong ESG performance experienced better financial performance and were less likely to go bankrupt.
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): CSR aligns with the United Nations' 17 Sustainable Development Goals, which aim to eradicate poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030. By incorporating CSR into their operations, companies can actively contribute to achieving these global goals.
What is the Purpose of Corporate Social Responsibility?
The purpose of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is multi-faceted and encompasses a range of objectives aimed at creating a positive impact on society, the environment, and various stakeholders. The primary purposes of CSR include:
- Social Impact: CSR aims to address and contribute to the resolution of social issues, such as poverty, education, healthcare, and inequality. By investing in social initiatives, companies can make a tangible difference in the lives of individuals and communities, helping to improve their well-being and overall quality of life.
- Environmental Stewardship: CSR focuses on promoting sustainable practices and reducing the ecological footprint of businesses. This includes initiatives to conserve resources, reduce emissions, adopt eco-friendly technologies, and protect biodiversity, all contributing to a healthier planet for future generations.
- Ethical Business Practices: CSR encourages companies to conduct business ethically and responsibly. It involves adhering to fair labor practices, respecting human rights, ensuring workplace safety, and maintaining transparent and honest relationships with stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Engagement: CSR fosters positive relationships with various stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, suppliers, and local communities. By involving stakeholders in decision-making processes and addressing their concerns, companies can build trust and strengthen their reputations.
- Long-Term Sustainability: CSR emphasizes the importance of sustainable business practices that consider long-term impacts rather than focusing solely on short-term profits. By prioritizing sustainability, companies can create a lasting and positive legacy for themselves and society.
Types of Corporate Social Responsibility
Archie B. Carroll, a prominent researcher in the field of corporate social responsibility (CSR), introduced the "pyramid of corporate social responsibility" in his influential article titled "The Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility," published in 1991.
Carroll's CSR pyramid is a theoretical framework that categorizes the different dimensions of CSR into four levels, each building upon the previous one. The four components of CSR in the pyramid are:
- Economic Responsibility: The base of the pyramid represents a company's fundamental responsibility to be profitable and economically viable. It emphasizes the importance of generating profits, ensuring financial stability, and delivering value to shareholders and stakeholders.
- Legal Responsibility: The second level of the pyramid refers to a company's obligation to comply with laws, regulations, and ethical standards. Companies must operate within the boundaries set by society and follow all applicable legal requirements.
- Ethical Responsibility: The third level highlights the significance of conducting business with fairness, integrity, and ethical conduct. Beyond mere compliance with the law, companies are expected to make ethical decisions and treat stakeholders, employees, customers, and communities with honesty and respect.
- Philanthropic Responsibility: The pinnacle of the pyramid represents the discretionary and voluntary aspect of CSR. At this level, companies undertake philanthropic initiatives, such as donating to charitable causes, supporting community development projects, and engaging in social welfare activities that go beyond their basic responsibilities.
Carroll's pyramid provides a comprehensive view of CSR, illustrating that being socially responsible involves more than just financial success and legal compliance. It emphasizes that ethical behavior and social contributions are equally crucial components of a company's overall responsibility towards society and stakeholders.
Corporate Social Responsibility Benefits
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) offers numerous benefits to both companies and society. Some of the key benefits include:
- Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image: Engaging in CSR initiatives can improve a company's reputation and brand image. By demonstrating a commitment to social and environmental issues, companies can build trust and goodwill among customers and stakeholders.
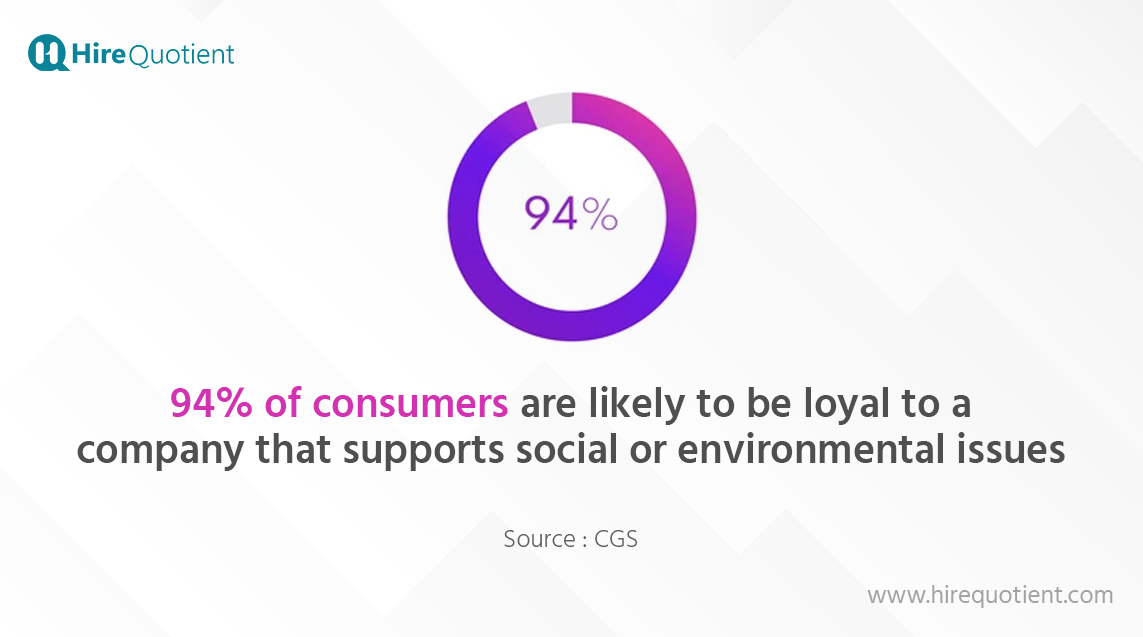
- Increased Customer Loyalty and Trust: Consumers are more likely to support and remain loyal to companies that actively contribute to social and environmental causes. CSR can positively influence consumer perceptions and foster long-term relationships with customers.
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: CSR programs can boost employee morale and job satisfaction. Employees tend to be more engaged and motivated when they work for a company that aligns with their values and contributes positively to society.

- Attraction and Retention of Talent: Companies that prioritize CSR are often more attractive to prospective employees, especially among younger generations who place a high value on social and environmental responsibility. Such companies can also experience better employee retention rates.
Tips for Building a Socially Responsible Business
Building a socially responsible business involves integrating ethical, environmental, and social considerations into the core of your company's operations and decision-making processes. Here are some tips to help you establish a socially responsible business:
- Define Your Values and Mission: Clearly define your company's values and mission, incorporating social responsibility as a fundamental pillar. Ensure that these values are communicated consistently across all levels of the organization.
- Engage Stakeholders: Identify and engage with stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and local communities. Understand their expectations and concerns regarding social and environmental issues to develop relevant CSR initiatives.
- Implement Ethical Business Practices: Uphold high ethical standards in all aspects of your business, from supply chain management to marketing and customer relations. Ensure transparency and accountability in your operations.
- Minimize Environmental Impact: Adopt eco-friendly practices to minimize your company's environmental footprint. This can include energy conservation, waste reduction, recycling programs, and sustainable sourcing.
- Support Employee Well-being: Prioritize the well-being of your employees by providing a safe and inclusive work environment, fair wages, opportunities for personal and professional development, and work-life balance.
- Respect Human Rights: Ensure that your company respects and promotes human rights both within the organization and throughout the supply chain. Avoid engaging in exploitative practices or supporting suppliers with unethical labor practices.
- Contribute to Local Communities: Engage in community development initiatives that address the specific needs of the communities where your business operates. Support local education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social programs.
- Set Measurable Goals: Establish clear and measurable CSR goals and track your progress regularly. This helps you monitor the impact of your initiatives and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
- Collaborate with NGOs and Government Agencies: Partner with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and government agencies to leverage their expertise and resources in addressing social and environmental challenges.
- Promote Diversity and Inclusion: Foster a diverse and inclusive workplace that values employees from various backgrounds and perspectives. Embrace diversity as a strength and promote equality in all aspects of your business.
- Responsible Marketing and Communication: Ensure that your marketing and communication strategies accurately represent your company's CSR efforts and avoid misleading claims or greenwashing.
- Measure and Report on Impact: Regularly measure and report on the social and environmental impact of your CSR initiatives. Transparent reporting builds trust with stakeholders and showcases your commitment to social responsibility.
What to avoid when creating a socially responsible business model?
When creating a socially responsible business model, it's crucial to avoid certain pitfalls and missteps that could undermine the integrity and effectiveness of your CSR efforts. Here are some key things to avoid:
- Greenwashing: Avoid making false or exaggerated claims about your company's social and environmental initiatives. Greenwashing, or misleading customers into believing your business is more socially responsible than it actually is, can lead to loss of trust and credibility.
- Tokenism: Don't engage in superficial or token CSR efforts merely to create a positive image. Social responsibility should be integrated genuinely into your business practices rather than being used as a marketing tool.
- Ignoring Stakeholder Input: Failing to engage with stakeholders and ignoring their input and concerns can lead to misguided CSR initiatives that do not address the real needs and expectations of the communities and other stakeholders.
- Disregarding Human Rights: Avoid engaging with suppliers or partners that violate human rights, practice child labor, or exploit workers. Uphold ethical standards throughout your supply chain.
- Short-term Focus: Don't view CSR as a short-term strategy for quick gains. Social responsibility is a long-term commitment that requires consistent efforts and dedication.
- Neglecting Employee Welfare: Your CSR efforts should extend to the well-being of your employees. Avoid practices that compromise employee safety, fair compensation, and work-life balance.
- Overlooking Environmental Impact: Ensure that your business considers its environmental impact in all aspects of operations. Avoid practices that harm the environment or contribute to pollution.
- Lack of Transparency: Be transparent about your CSR initiatives and their outcomes. Avoid hiding negative impacts or failing to disclose relevant information to stakeholders.
- Conflicting Values: Ensure that your CSR initiatives align with your company's core values and mission. Avoid supporting causes or projects that contradict your stated principles.
- Relying Solely on Philanthropy: While philanthropy has its place, avoid relying solely on donations or charitable giving without addressing the root causes of social and environmental issues.
Disadvantages Of CSR
While Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has many benefits, it also comes with certain disadvantages and challenges that businesses need to be aware of:
- Financial Costs: Implementing CSR initiatives can be expensive. Companies may need to invest significant resources in social and environmental programs, which could impact profitability in the short term.
- Diverted Focus: Some argue that focusing on CSR initiatives might divert a company's attention from its core business objectives, potentially leading to reduced competitiveness or missed opportunities.
- Greenwashing and Cynicism: Companies that engage in greenwashing or insincere CSR efforts risk facing skepticism and cynicism from customers and stakeholders, which can harm their reputation.
- Difficulties in Measuring Impact: It can be challenging to accurately measure the impact of CSR initiatives. Without clear metrics and data, it becomes challenging to assess the effectiveness of these efforts.
- Time-Consuming: Developing and maintaining effective CSR initiatives require time and effort, diverting management's attention from other crucial business activities.
Corporate Social Responsibility Theory
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) theory is a framework that explores the ethical and moral responsibilities of businesses toward society and the environment. It suggests that companies have an obligation to go beyond profit-making activities and consider their impact on various stakeholders, including employees, customers, communities, and the environment. CSR theory emphasizes that businesses should take into account social and environmental concerns while conducting their operations and making decisions.
Key principles and concepts of CSR theory include:
- Stakeholder Approach: The stakeholder approach posits that businesses have responsibilities not only to shareholders but also to a broader group of stakeholders. This includes employees, customers, suppliers, local communities, government, and other parties affected by the company's actions.
- Triple Bottom Line: CSR theory adopts the concept of the triple bottom line, which focuses on measuring a company's success based on three dimensions: economic, social, and environmental performance. Instead of solely emphasizing financial profits, the triple bottom line considers the company's impact on people and the planet.
- Sustainability: CSR theory emphasizes the importance of sustainable development, ensuring that businesses meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. It calls for responsible resource management and environmental protection.
- Ethical Behavior: CSR theory advocates for ethical business practices, encouraging companies to act with integrity and transparency in all aspects of their operations. This includes fair treatment of employees, honesty in marketing and advertising, and responsible sourcing.
- Voluntary Initiatives: While CSR can be influenced by laws and regulations, CSR theory encourages businesses to take voluntary actions that go beyond legal requirements. It highlights the importance of companies proactively addressing social and environmental challenges.
- Philanthropy and Community Engagement: CSR theory recognizes the role of businesses in contributing to the welfare of society through charitable giving, community development projects, and other philanthropic activities.
- Long-Term Perspective: CSR theory encourages companies to adopt a long-term perspective, recognizing that sustainable business practices can lead to improved reputation, customer loyalty, and overall business success in the long run.
- Shared Value: CSR theory supports the concept of "shared value," where companies create economic value while simultaneously addressing social and environmental challenges. Shared value initiatives align business goals with societal needs.
CSR Problems And Solutions
There are multiple corporate social responsibility, but companies can implement several solutions to address these problems effectively. Here are some common CSR problems and potential solutions:
Problem: Lack of Clear Strategy and Focus
Solution: Develop a comprehensive CSR strategy aligned with the company's core values and business objectives. Identify key areas of impact and set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each initiative.
Problem: Insufficient Resources
Solution: Allocate sufficient financial and human resources to support CSR initiatives. Consider integrating CSR into the company's budgeting process and invest in long-term projects that align with the company's priorities.
Problem: Greenwashing and Lack of Transparency
Solution: Avoid greenwashing by being transparent about CSR efforts. Accurately communicate the company's achievements and challenges, and provide data and metrics to support claims. Engage third-party audits to validate CSR performance.
Problem: Difficulty in Measuring Impact
Solution: Develop robust metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the social and environmental impact of CSR initiatives. Regularly assess and report on progress toward achieving CSR goals.
Problem: Balancing Stakeholder Expectations
Solution: Engage with stakeholders to understand their expectations and concerns. Prioritize the most critical issues and involve stakeholders in decision-making processes. Regularly communicate with stakeholders to update them on progress.
CSR certifications
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) certifications are third-party validations that recognize a company's commitment to responsible and sustainable business practices. These certifications provide credibility and transparency, assuring stakeholders that the company is meeting specific CSR standards and criteria. Some of the prominent CSR certifications include:
- B Corp Certification: B Corp certification is awarded to businesses that meet high standards of social and environmental performance, accountability, and transparency. B Corp-certified companies undergo a rigorous assessment by the non-profit organization B Lab to ensure their commitment to responsible practices.
- ISO 26000: ISO 26000 is a global standard providing guidance on social responsibility. Companies that align their practices with ISO 26000 demonstrate their dedication to addressing social, environmental, and ethical considerations.
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC): The UNGC is a voluntary initiative that encourages businesses to adopt sustainable and socially responsible policies and practices. By signing the compact, companies commit to aligning their operations with ten universally accepted principles in the areas of human rights, labor, environment, and anti-corruption.
- Carbon Neutral Certification: This certification is awarded to companies that achieve carbon neutrality by reducing their greenhouse gas emissions and offsetting the remaining emissions through verified carbon offset projects.
- Fair Trade Certification: Fair Trade certification applies mainly to companies involved in producing and trading commodities. It guarantees that products have been sourced and traded in a manner that supports fair wages, safe working conditions, and sustainable environmental practices for producers in developing countries.
- Rainforest Alliance Certification: The Rainforest Alliance certification is granted to companies that meet strict environmental and social standards in agricultural and forestry practices. It focuses on promoting biodiversity conservation, protecting ecosystems, and improving the livelihoods of farmers and workers.
- LEED Certification: While primarily focused on buildings and construction, LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification recognizes companies for their commitment to sustainability, energy efficiency, and green building practices.
- Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI) Base Code: The ETI Base Code sets out nine principles covering labor rights, working conditions, and environmental performance. Companies adhering to this code demonstrate their commitment to ethical sourcing and responsible supply chain management.
- SA8000: SA8000 is a social accountability standard developed by Social Accountability International (SAI). It certifies companies that meet specific requirements related to labor conditions, health and safety, child labor, and fair remuneration.
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): GRI provides guidelines for companies to report on their economic, environmental, and social performance. While not a certification, following GRI guidelines enhances the transparency and credibility of a company's CSR reporting.
Examples of Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) can take various forms, and companies implement a wide range of initiatives to contribute positively to society and the environment. Here are some examples of CSR initiatives:
- Environmental Sustainability: Implementing eco-friendly practices to reduce the company's environmental impact. This can include using renewable energy, reducing waste, recycling, and adopting sustainable sourcing and production methods.
- Employee Volunteer Programs: Encouraging employees to engage in volunteer activities in their local communities or participate in environmental conservation projects.
- Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and providing opportunities for professional development and training for employees.
- Community Development: Investing in local communities through projects that address their needs, such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and job creation.
- Charitable Giving: Donating a portion of profits or products to charitable organizations that focus on various social and environmental causes.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promoting diversity and inclusion within the company by implementing policies that support gender equality, ethnic diversity, and inclusive hiring practices.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that suppliers and business partners adhere to ethical and sustainable practices, particularly in industries like fashion and agriculture.
- Education and Skills Training: Supporting educational programs and skills training initiatives that empower disadvantaged individuals and communities.
- Support for Nonprofits and NGOs: Providing financial or in-kind support to non-profit organizations and NGOs working on social and environmental issues.
- Social Impact Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses, governments, and non-profits to address complex social and environmental challenges more effectively.
- Responsible Marketing: Avoid deceptive marketing practices and ensure that advertising accurately represents the company's CSR initiatives.
- Philanthropic Investments: Allocating funds to support scientific research, environmental conservation, or social innovation that aligns with the company's mission and values.
- Supplier Audits: Conduct audits and assessments of suppliers to ensure they comply with labor and environmental standards.
- Disaster Relief Support: Providing aid and resources in response to natural disasters or other emergencies affecting communities where the company operates.
- Ethical Business Practices: Ensuring ethical conduct in all business operations and supply chain management, such as combatting corruption and respecting human rights.
Brands doing Corporate Social Responsibility
Many well-known brands and companies actively engage in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Here are some examples of brands that have demonstrated their commitment to CSR:
- Patagonia: Patagonia is known for its commitment to environmental conservation. The company donates a percentage of its profits to environmental causes, supports grassroots environmental campaigns, and encourages customers to repair and recycle their products to reduce waste. They also promote Fair Trade practices in their supply chain.
- Unilever: Unilever has made sustainability a core part of its business strategy. The company has set ambitious goals to reduce its environmental impact, such as halving the environmental footprint of its products and improving the livelihoods of smallholder farmers through various initiatives.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola has several CSR initiatives, including water stewardship programs to protect water resources in communities where they operate. They also invest in community development projects focused on education, health, and economic empowerment.
- LEGO: LEGO is committed to sustainability and responsible sourcing of materials. They aim to make all their products from sustainable materials by 2030 and invest in educational programs to support children's education and play.
To conclude,
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a fundamental concept that transcends the traditional notion of profit-making in business. It represents a transformative approach where companies take on the responsibility of positively impacting society and the environment while achieving their financial goals. CSR is not a mere add-on or a marketing tool; rather, it is a genuine commitment to ethical, sustainable, and socially responsible practices.

